What is consumer choice? How has globalization expanded consumer choice? What role does technology play in enhancing consumer choice?
Globalization has transformed the consumer landscape, offering a wider variety of products and more affordable prices than ever before. The interconnected global market has brought greater access to innovations, driven competition, and raised quality standards, resulting in an enhanced shopping experience for consumers everywhere.
In this blog, we explore the positive effects of globalization on consumer choice and pricing. It has expanded product variety, increased affordability, and accelerated the spread of technology, ultimately reshaping the way we live and shop today.
All of the facts and figures about how globalization has benefited consumer choice cannot do the job as well as this simple thought experiment:
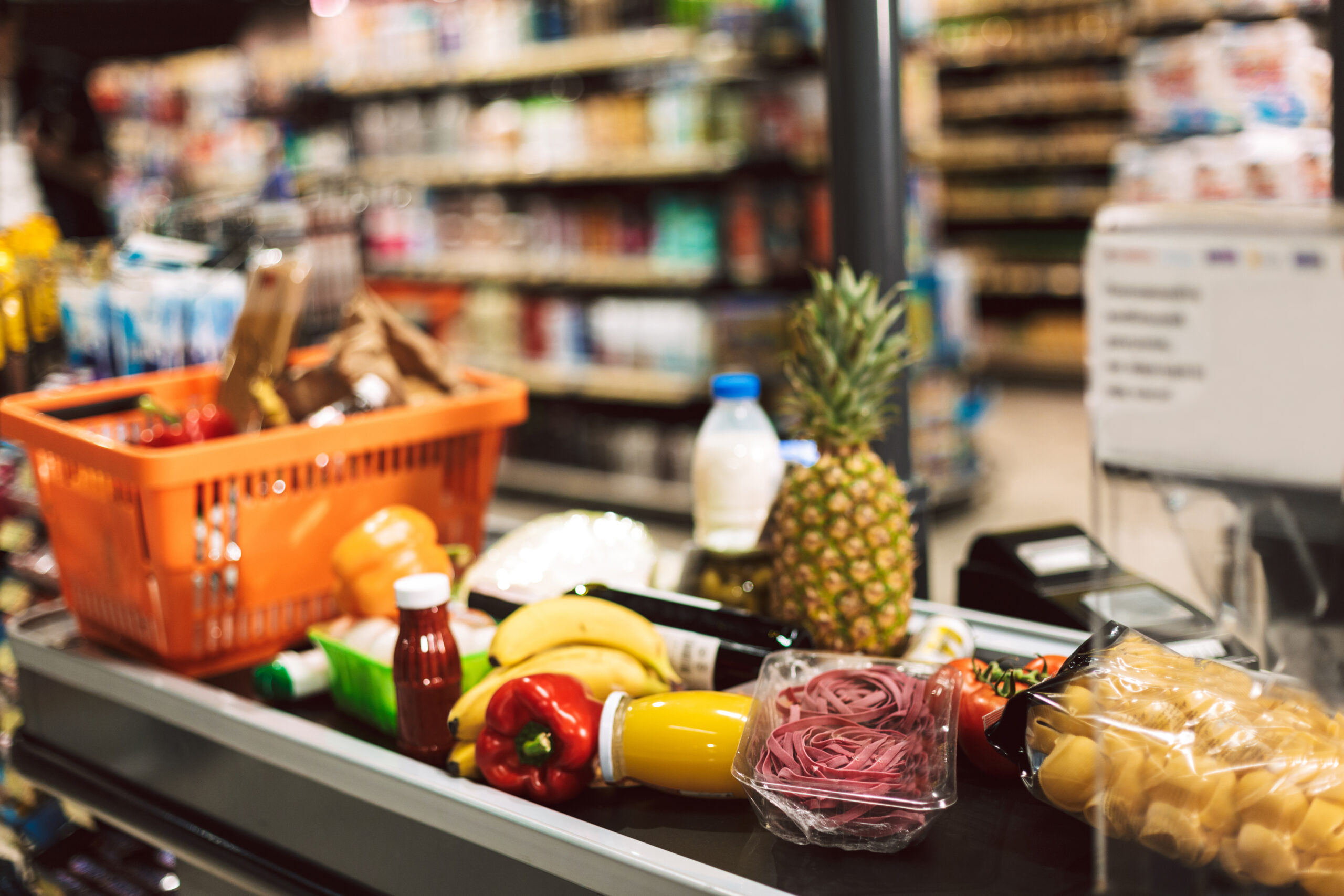
Imagine you are standing in a well-maintained local supermarket near where you live. Look around. Really, look around as though you were seeing it for the first time. The shelves around you are stocked with olive oil produced from hundred-year-old olive trees in the sunbaked foothills of Sicily. In the next aisle, a dozen roasts of coffee from the rich soils of Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru sit side by side. Maple syrup from Canada. Spices sourced from the Middle East. Bananas from Guatemala. High-quality electronics from Japan. All within a short walk of where you are standing.
This visualization is a snapshot of globalization’s fruits (including some literal fruits!) in action. A painstakingly built and interconnected pathway of supply chains and production efficiencies has created a world where access to products from nearly any corner of the globe is now taken for granted. The consumer choice we are presented with has come a long way in a hurry.
The surge in global trade has allowed producers from different countries to reach broader markets and expand the range of choices available. The efficiencies of scale and specialization have also enabled more competitive pricing.
The following discussion aims to further highlight the key ways globalization has positively impacted consumer choice and affordability and the positive net effects on how we live our lives today.
Table of Contents:
Enhanced Access to Technological Innovation
Competitive Pricing Due to Increased Market Access
Improvement in Quality Standards
Economies of Scale and Lower Production Costs
Expansion of Product Variety
Globalization has meant that consumer choices have expanded in ways that would have been unimaginable to our parents or grandparents. The car industry provides an obvious example of this. American auto manufacturing was once the sole choice for North American consumers. The number of options available to consumers expanded as Japanese, Korean, and now Chinese automakers entered the market at scale. Competition lowered prices, even as choice expanded.
Companies from different parts of the world entering new markets bring unique products, styles, and technologies that reflect their own cultural and industrial strengths. It’s not just traditional manufacturing that benefits from this dynamic. Fashion, music, technology, and food also benefit from this cross-pollination of ideas and increased diversity.
This expanded product variety extends beyond niche items and luxury goods to essentials and everyday products, enriching daily life by offering options that reflect varying preferences and needs.
Enhanced Access to Technological Innovation
Globalization has also dramatically accelerated the spread of technological innovation, enabling consumers worldwide to access cutting-edge products and services far more quickly than in the past. Technological advancements developed in one region can rapidly be made available to consumers away from ‘home’ markets when a global market is in play. This rapid distribution and ability to serve a global marketplace is largely thanks to the work it has taken over decades to streamline supply chains and develop an interconnected world economy.
One prime example of this is the smartphone market. Ten years ago, Apple’s iPhone was primarily viewed as a luxury item in many regions due to its high price and limited availability. However, with increased competition from global brands like Xiaomi, Huawei, and Samsung, consumers worldwide now have access to a vast selection of smartphones with comparable technology and features at various price points. This competition has driven prices down, allowing for an estimated 4.5 billion smartphone users globally in 2024, which is set to grow further in the coming years.
Another example is the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). The development and manufacturing of EVs were initially concentrated in a few regions that possessed traditional automotive manufacturing bases, notably the U.S. and Western Europe. However, with these locations came high costs, which in turn limited accessibility for global consumers.
However, the EV landscape has transformed as manufacturers like Tesla, BYD (China), and Nissan expanded production to new markets. In 2023, China alone produced nearly 9 million EVs, making up over 50% of the global output. As economies of scale were reached, costs came down. If the trend holds, global EV sales are projected to reach over 30 million by 2030. Globalization’s role in shortening development cycles and speeding up technology transfer has enabled countries to adopt this innovation more quickly. This is driven by simple mathematics and logic. Suppose an economy of scale is needed to bring the unit costs of a product down. In that case, having the entire globe as a target market is beneficial because it increases the likelihood of achieving that economy of scale more rapidly.
Now, let’s consider a slower example of the rollout of a similarly cutting-edge technology in its time: the television set. Television technology was initially limited to a few wealthy countries where the government could afford to build the infrastructure to support it, and citizens could afford to pay for the product. The infrastructure required to produce and distribute TVs was costly and localized. It wasn’t until the late 20th century, several decades after its introduction, that television became globally accessible and affordable.
Competitive Pricing Due to Increased Market Access
Perhaps the most welcome benefit of globalization to purchasers (other than increased consumer choice) is lower prices. When products from international markets enter domestic markets, they drive competition. Specifically, the competition pushes local businesses to either improve quality or reduce prices to remain competitive. Both are positive for the consumer.
Many of you may have clearly felt this effect related to the consumer electronics industry. In the 1990s, high import tariffs and limited international competition kept prices for personal computers and other electronics elevated in many markets. With the expansion of trade agreements and reduced tariffs in the early 2000s, companies like Dell, Lenovo, and Acer entered multiple markets worldwide, introducing pricing pressures that made computing devices accessible to a much broader consumer base. Consequently, the average price of a personal computer dropped from around $1,600 in the early 1990s to under $500 today. This has occurred while computing power and quality have increased exponentially.
Increased competition also compels companies to invest in product development to differentiate themselves and capture consumer interest. Innovation benefits the consumer through better quality options and lower prices. Quality deserves more attention as it is often overlooked.
Improvement in Quality Standards
Global competition has created an environment where companies are driven to offer competitive prices and consistently elevate the quality of their products. In a world where consumers can easily access alternatives from various international markets, quality becomes a defining factor for success, and a poor-quality experience likely creates a long-term aversion to that product and brand.
This push for quality is often formalized through widely adopted quality standards, which have become a hallmark of globalization. For instance, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) sets internationally recognized standards in everything from safety to environmental performance, ensuring a level of quality that consumers can trust across borders.
Take ISO 9001, one of the most recognized quality management standards globally. This certification ensures that products meet a certain level of quality and consistency by evaluating and auditing processes within companies to help them maintain high standards. ISO 9001 certification has been particularly significant in manufacturing, healthcare, and electronics, where adherence to this standard helps guarantee that consumers receive safe and reliable products. For example, a consumer purchasing a medical device can feel confident in its efficacy and safety if an ISO-certified company produces it. It’s not just nice to have. This level of certification is especially valuable in critical fields like medicine and pharmaceutical research, where the precision of instruments and machines is literally a life-or-death matter.
Another tangible example is the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) standard. This is an essential guideline in the global food industry. HACCP is adopted widely, and its guidelines ensure rigorous safety and sanitation practices. The experience of Chipotle and its customers in the mid-2010s and the fine of $25 million they paid highlights the tangible financial risks of getting food safety wrong. This HACCP standard has enabled consumers worldwide to enjoy diverse foods from around the globe with minimal safety concerns. Knowing that imported food products adhere to HACCP or similar safety standards provides consumers with a sense of security and broadens their choices in foods they can trust to be safe, which enhances the quality of the consumer’s choice on offer.
By adhering to these global quality standards, companies provide consumers with peace of mind that their products are dependable and safe. This emphasis on quality, reinforced by global competition, results in a market filled with options that meet high standards, allowing consumers to enjoy both quality and affordability in products across various sectors.
Economies of Scale and Lower Production Costs
One of globalization’s most significant consumer benefits is the ability of companies to achieve economies of scale. This might seem abstract, but it is the key mechanism that allows for lower production costs, which in turn feeds into lower prices for consumers.
When companies expand their operations across borders, they can increase their production volume, allowing them to distribute fixed costs over larger units. This efficiency reduces the cost per unit, lowering store shelves’ prices. Companies like Apple and Samsung operate globally, producing millions of units of each device model. Components are sourced in bulk, production processes are streamlined, and end-user costs fall.
Global outsourcing and manufacturing efficiencies also play a pivotal role in reducing production costs. Companies can cut operational expenses by outsourcing production to countries with lower labor costs. For instance, clothing brands often manufacture their products in regions where production costs are comparatively lower and where a larger workforce specializes in the skills required to produce textiles. This strategic approach allows brands to keep prices accessible for consumers while remaining competitive in the global market.
This ripple effect of reduced production costs benefits large corporations and positively impacts small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that rely on competitive pricing to attract consumers. With access to more affordable global suppliers, SMEs can pass these savings to their customers, creating a broader array of competitively priced products. These economies of scale ultimately deliver consumers access to a greater selection of products at prices that fit within more budgets.
Key Takeaways
Globalization has reshaped the consumer experience by greatly expanding consumer choice and reducing prices.
From the explosion of product variety and access to cutting-edge technologies to competitive pricing and stringent quality standards, consumers today enjoy more diverse and affordable options than ever before. Globalization’s impact on economies of scale and production costs has driven competition, which keeps prices accessible while maintaining high-quality standards across products.
These benefits of globalization enhance the overall consumer experience by broadening access to products, creating a sense of value, and promoting trust in the quality of goods available. As global markets continue to evolve, consumers will likely see even more innovative products, competitive pricing, and improved quality standards—making globalization an enduringly positive force for consumers worldwide.
And if you ever need to be reminded of any of the above, I encourage you to occasionally wander the aisles of your favorite grocery, hardware, or home furnishings store with a sense of curiosity to really ‘see’ with fresh eyes what is available to you. That sense of discovery may help you ponder how many invisible hands, across many countries, working in concert, it took to bring you the myriad choices available to you in those aisles.